key moments
-
Recession. Economy could fall 0.9% in adverse scenario, says ECB -
The central scenario is not a recession but the ECB admits another “very dark” adverse scenario -
Lagarde stresses that state support must be temporary and not worsen inflation -
ECB admits “stagnation” of the economy at the end of this year and the beginning of 2023 -
The ECB does not stop there. “Interest rates should go back up” because inflation remains “too high” -
75 basis points. The ECB announces the biggest interest rate hike in its history -
The new projections should not (for now) predict a recession
live updates
1 in
1
-
The euro falls after Jay Powell, in the US, guaranteed his commitment to the fight against inflation
Even with an interest rate hike of 75 basis points, the largest in the history of the eurozone, the single currency quote took a downward trend after the leader of the Federal Reserve, Jerome (“Jay”) Powell, assured that the US central bank will continue to tighten monetary policy to control inflation expectations.
“History clearly shows how not to ease monetary policy prematurely,” Powell said, leaving his “assurance” that both the Fed chairman and other central bank officials “are strongly committed to this mission and we will continue until the work is done.” finished”.
In Frankfurt, Christine Lagarde went beyond the usual when acknowledging that the ECB is attentive to the evolution of the price of the euro, because the recent devaluation of the single currency is “something that contributes to the accumulation of inflationary pressures”. Despite this, the euro fell below par again, falling 0.7% to $0.995.
-
Recession. Economy could fall 0.9% in adverse scenario, says ECB
The eurozone economy could contract by 0.9% in 2023, according to an “adverse scenario” developed by ECB economists and described by Christine Lagarde as “very grim” (emphasizing that it is not the central scenario).
As soon as Christine Lagarde’s press conference in Frankfurt ended, the macroeconomic projections were published showing the negative value for 2023: -0.9% (with inflation of 6.9%).
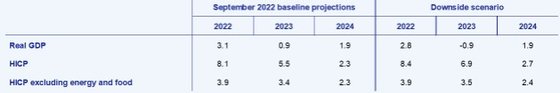
This more negative scenario is a projection that tries to simulate what the economic evolution will be if the war in Ukraine becomes “very prolonged” and geopolitical tensions continue.
“It is assumed that all current sanctions are maintained, which would translate into larger and more lasting economic shocks in the eurozone,” clarifies the ECB, explaining how that value of -0.9% was reached.
“It is a scenario that includes an increase in uncertainty, which translates into a significant adjustment of the risk premiums implicit in the cost of financing companies and in the equity markets, with a deterioration in financial conditions”, adds the ECB.
-
The central scenario is not a recession but the ECB admits another “very dark” adverse scenario
The new ECB macroeconomic projections will be released in detail at 14:45 (Lisbon time) but it is already known that even in 2023 economists point to a (positive) growth of 0.9%.
However, Christine Lagarde confirmed that the ECB economists simulated a adverse scenario – which includes events such as the total cut off of Russian gas and energy rationing in Europe and does not foresee compensatory phenomena (such as the increase in energy supply from other geographies).
that’s one”very black landscapewhich, Lagarde emphasizes, is not the central scenario and, there, in fact, there is a forecast of negative growth (economic recession).
-
-
Lagarde stresses that state support must be temporary and not worsen inflation
Christine Lagarde stressed, at the press conference in Frankfrut, that the State supports governments decide to jump into economies must be temporary and must not worsen inflation.
The inflation figures are “extraordinarily high” and are also spilling over into the prices of services (not just goods), Christine Lagarde said, speaking an unusually somber tone for the one she usually delivers at regular ECB press conferences. .

-
Exchange. Euro with little reaction to expected increases in interest rates
The euro-dollar exchange rate is oscillating at the parity level, that is, exactly one euro for one dollar – The increase in interest rates by the ECB, of 75 basis points, was already expected by most analysts, so the foreign exchange markets outlined a relatively contained reaction to the announcement.
In addition, on the other side of the Atlantic, a speech by Jay Powell, the head of the US Federal Reserve, is also expected, so investors in the currency markets await the content of this message to assume new relevant positions in one. direction or the other. .
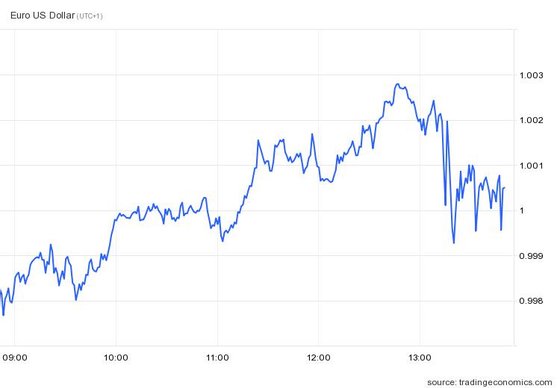
Euro-dollar pair in intraday evolution. SOURCE: TradingEconomics
Christine Lagarde referred, in the press conference, that the recent weakness of the euro “has contributed” to the accumulation of inflationary pressures.
-
ECB admits “stagnation” of the economy at the end of this year and the beginning of 2023
The new ECB forecasts point to a growth of the eurozone economy of 3.1% in 2022, to then fall to 0.9% in 2023. As for 2024, the forecast was reduced to 1.9%.
“After a recovery in the first half of 2022, recent data points to a significant slowdown in economic growth in the eurozone, with the economy expected to stall in the final phase of this year and in the first quarter of 2023”, says the ECB in the statement report.
-
The ECB does not stop there. “Interest rates should go back up” because inflation remains “too high”
The ECB confirms, also in the statement, that the “interest rates will continue to rise“, as inflation “remains too high and is likely to remain above target for an extended period”.
“Our future monetary policy decisions will depend on economic data,” says the ECB.
The new inflation forecasts, also published this Thursday, are for a price increase of 8.1% in 2022, 5.5% in 2023 and 2.3% in 2024 -that is, not even in 2024 does the ECB believe that inflation will remain in the middle. target deadline.
-
75 basis points. The ECB announces the biggest interest rate hike in its history
75 basis points. The European Central Bank (ECB) has just confirmed the biggest rise in the history of reference interest rates: three quarters of a percentage point.
The interest rate on deposits, which in recent years has become the main tool of the ECB’s monetary policy, thus falls to 0.75%. The key refinancing rate is now 1.25%, having also risen 75 basis points.
In a statement, the ECB acknowledges that this is a “giant step” that accelerates the “transition from a very accommodative level of interest rates to levels that ensure a timely return of inflation to the ECB’s medium-term objective, which is 2%”.
-
The new projections should not (for now) predict a recession
In addition to the decision on interest rates, this regular meeting of the ECB includes the publication of new quarterly economic projections, prepared by the staff of central bank economists.
It is expected that there will be a strong downward revision of the growth projections for 2023. Therefore, this revision will have to continue to point to a positive growth, despite several advanced indicators in the European economy, analysts will expect an economic recession not to start next year.
Read here the text published last night, about the “incredibly difficult situation” in which the ECB finds itself, having to raise interest rates knowing that there is a risk of recession, which is not even the only risk that worries Christine Lagarde .
Inflation, risk of recession and fall of the euro. In an “incredibly difficult situation”, the ECB will go ahead with a new rate hike
-
The ECB raises interest rates again. Will it be 50 or 75 basis points?
Buenas tardes,
The European Central Bank (ECB) will soon announce a new rise in interest rates. This is a certainty, the question is whether it will be a new increase in 50 basis pointsas in July, or if it will be 75 basis points (three-quarters of a percentage point), which would be the largest rise in the history of the eurozone.
Let’s follow the minute decision, to be announced at 13:15 (Lisbon time)with a press conference from Frankfurt starting half an hour later.
Thank you very much for following our coverage.
1 in
1
- Advertisement -

